How to Write the Method Section of a Literature Review
How to write the methods department of a systematic review
- How To
Home | Weblog | How To | How to write the methods section of a systematic review
Covidence breaks down how to write a methods department
The methods section of your systematic review describes what you did, how yous did information technology, and why. Readers demand this data to interpret the results and conclusions of the review. Often, a lot of information needs to be distilled into just a few paragraphs. This can be a challenging task, but proficient preparation and the right tools will help you to set off in the right direction 🗺️🧭.
Systematic reviews are and then-called because they are conducted in a way that is rigorous and replicable. And then information technology's important that these methods are reported in a way that is thorough, clear, and like shooting fish in a barrel to navigate for the reader – whether that'southward a patient, a healthcare worker, or a researcher.
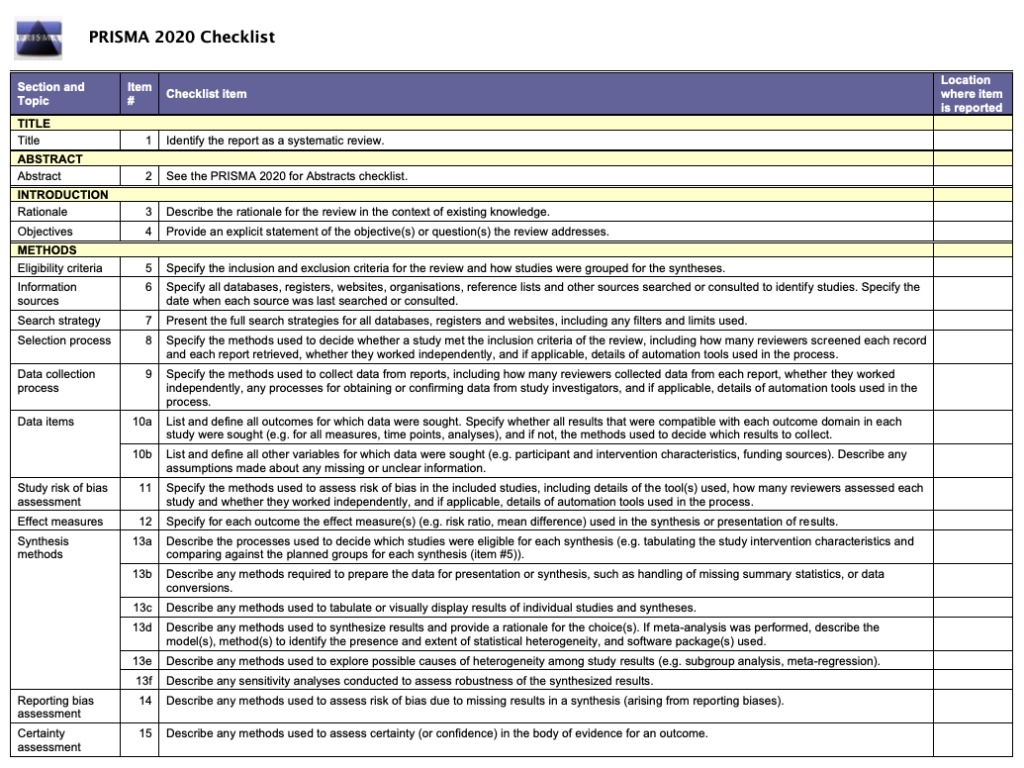
Like most things in a systematic review, the methods should be planned upfront and ideally described in detail in a project programme or protocol. Reviews of healthcare interventions follow the PRISMA guidelines for the minimum set of items to written report in the methods section. Just what else should be included? It's a good idea to consider what readers will desire to know about the review methods and whether the journal y'all're planning to submit the work to has expectations on the reporting of methods. Finding out in advance volition help you lot to plan what to include.
Describe what happened
While the inquiry plan sets out what you lot intend to do, the methods section is a write-up of what actually happened. It's not a unproblematic case of rewriting the plan in the past tense – y'all will also need to talk over and justify deviations from the programme and describe the handling of issues that were unforeseen at the time the programme was written. For this reason, it is useful to make detailed notes before, during, and subsequently the review is completed. Relying on memory solitary risks losing valuable information and trawling through emails when the deadline is looming can be frustrating and fourth dimension consuming!
Keep it brief
The methods department should exist succinct merely include all the noteworthy information. This can be a difficult balance to achieve. A useful strategy is to aim for a cursory description that signposts the reader to a separate department or sections of supporting information. This could include datasets, a flowchart to evidence what happened to the excluded studies, a collection of search strategies, and tables containing detailed information virtually the studies.This separation keeps the review short and simple while enabling the reader to drill downward to the detail as needed. And if the methods follow a well-known or standard process, information technology might suffice to say so and requite a reference, rather than depict the procedure at length.
Follow a construction
A clear construction provides focus. Utilise of descriptive headings keeps the writing on track and helps the reader become to key data rapidly. What should the structure of the methods section expect like? As always, a lot depends on the type of review but it will certainly contain data relating to the following areas:
- Selection criteria ⭕
- Search 🕵️
- Data collection and analysis 👩💻
- Study quality and take chances of bias ⚖️
Allow'due south expect at each of these in turn.
1. Selection criteria ⭕
The criteria for including and excluding studies are listed here. This includes particular near the types of studies, the types of participants, the types of interventions and the types of outcomes and how they were measured.
2. Search 🕵🏾♀️
Comprehensive reporting of the search is important considering this ways it tin be evaluated and replicated. The search strategies are included in the review, forth with details of the databases searched. Information technology's also important to list any restrictions on the search (for example, language), describe how resources other than electronic databases were searched (for case, non-indexed journals), and give the engagement that the searches were run. The PRISMA-South extension provides guidance on reporting literature searches.
![]()
Systematic reviewer pro-tip:
Re-create and paste the search strategy to avoid introducing typos
3. Data drove and assay 👩💻
This section describes:
- how studies were selected for inclusion in the review
- how study data were extracted from the study reports
- how written report data were combined for analysis and synthesis
To describe how studies were selected for inclusion, review teams outline the screening procedure. Covidence uses reviewers' conclusion data to automatically populate a PRISMA menstruation diagram for this purpose. Covidence can also summate Cohen's kappa to enable review teams to report the level of agreement amid individual reviewers during screening.
To draw how study data were extracted from the study reports, reviewers outline the form that was used, any pilot-testing that was done, and the items that were extracted from the included studies. An important piece of data to include hither is the process used to resolve conflict amongst the reviewers. Covidence'southward data extraction tool saves reviewers' comments and notes in the system as they work. This keeps the information in one place for like shooting fish in a barrel retrieval ⚡.
To describe how study data were combined for analysis and synthesis, reviewers outline the blazon of synthesis (narrative or quantitative, for example), the methods for grouping information, the challenges that came upward, and how these were dealt with. If the review includes a meta-analysis, it volition detail how this was performed and how the treatment effects were measured.
four. Written report quality and risk of bias ⚖️
Because the results of systematic reviews can be affected by many types of bias, reviewers make every effort to minimise it and to show the reader that the methods they used were appropriate. This department describes the methods used to assess study quality and an assessment of the risk of bias across a range of domains.
Steps to assess the risk of bias in studies include looking at how study participants were assigned to treatment groups and whether patients and/or study assessors were blinded to the handling given. Reviewers as well study their cess of the risk of bias due to missing effect data, whether that is due to participant drop-out or not-reporting of the outcomes past the study authors.
Covidence'south default template for assessing report quality is Cochrane's risk of bias tool simply it is besides possible to get-go from scratch and build a tool with a set of custom domains if y'all prefer.
Determination
Conscientious planning, articulate writing, and a structured approach are primal to a skilful methods section. A methodologist volition exist able to refer review teams to examples of adept methods reporting in the literature. Covidence helps reviewers to screen references, excerpt data and consummate risk of bias tables speedily and efficiently. Sign upward for a complimentary trial today!

Laura Mellor. Portsmouth, Uk
I am a freelance editor and writer with 20 years' experience in academic publishing. I am the Editorial Assistant for the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. My favourite affair to do on the weekend is get up early on and go for a swim in the body of water. Twitter: @lauratorial.
Share...
Perhaps you'd also like...
Better systematic review management
Source: https://www.covidence.org/blog/how-to-write-the-methods-section-of-a-systematic-review/
0 Response to "How to Write the Method Section of a Literature Review"
Post a Comment